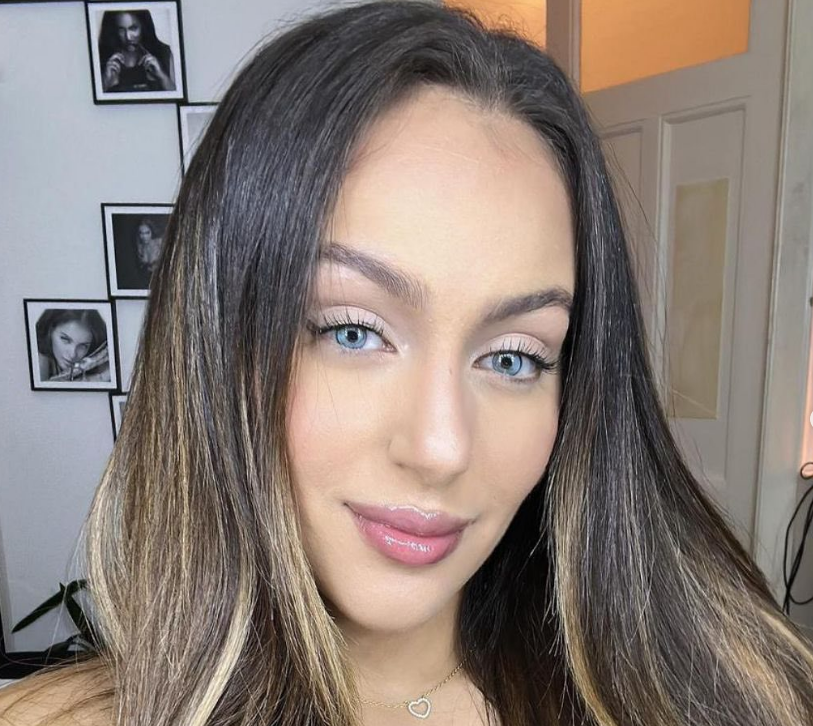
Eye color change procedure: what are the risks and danger?
The safety of eye color changing surgery can vary depending on the specific procedure used and the expertise of the surgeon performing it. Here are some key points to consider:
Different types of risks for difference types of eye color change techniques
- Keratopigmentation: Keratopigmentation is a relatively safe procedure when performed by a trained and experienced ophthalmologist using the right equipment and medical-grade pigments. It involves pigmenting the eye’s cornea to change its color. Safety largely depends on the clinic, surgeon, protocol, and technology used. Choosing a reputable clinic and surgeon is essential to minimize risks.
- Artificial Iris Implants: The safety of artificial iris implantation is more controversial. This procedure involves surgically implanting an artificial iris to change eye color. It is generally not recommended for purely cosmetic reasons and may carry risks, including potential complications like glaucoma, cataracts, and vision problems. It should only be considered in specific medical cases.
- Colored Contact Lenses: Colored contact lenses are generally safe when used as prescribed and obtained through a legitimate prescription from an eye care professional. However, using non-prescription colored contact lenses can pose significant risks, including eye infections, abrasions, ulcers, and even vision loss. Proper hygiene and adherence to prescription guidelines are crucial for safety.
- Laser Eye Surgery: Laser eye surgery for eye color change is another option, but it is associated with risks like uveitis, glaucoma, reduced vision, and, in extreme cases, potential blindness. Some ophthalmologists have raised concerns about its safety, and potential candidates should carefully consider these risks.
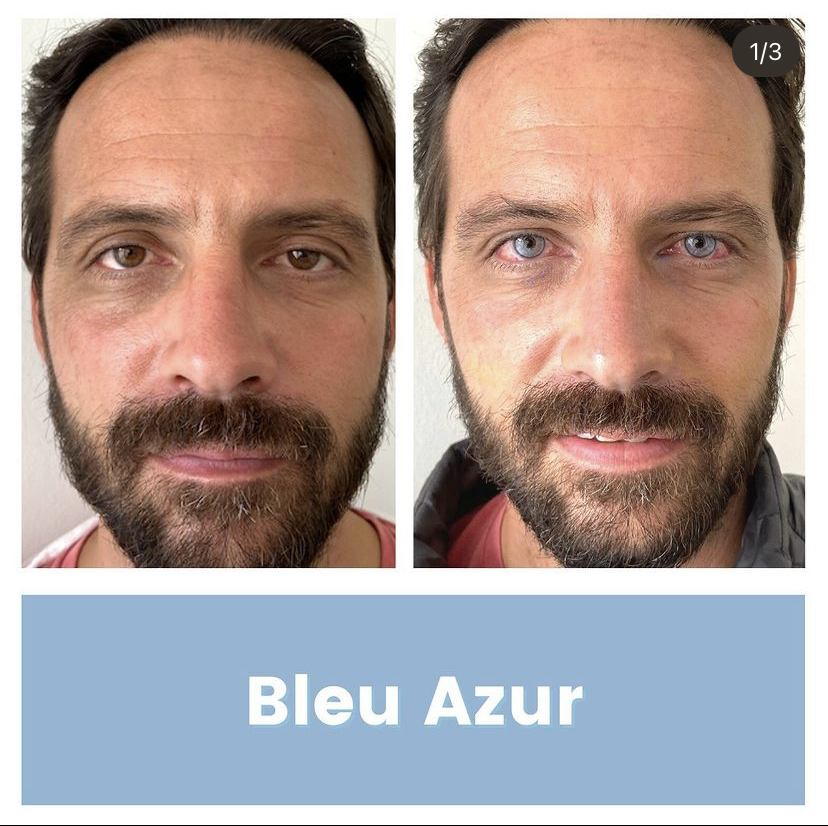

Various Techniques for Changing Eye Color: Are They Safe?
There are several surgical techniques available for changing eye color, and it’s essential to carefully consider the advantages, risks, and potential complications associated with each.
=> More about is Keratopigmentation a safe surgery?
Artificial Iris Implants: Is It a Safe Procedure?
Artificial iris implantation is a less common procedure that carries certain risks. In rare worst-case scenarios, it can result in blindness or reduced vision. Additionally, complications like cornea issues, cataracts, or glaucoma may arise.
Candidates for artificial iris transplant procedures should not have:
- Retinal detachment
- An eye infection
- Eye inflammation
- An eye disorder affecting eye function (e.g., rubella cataract)
- Rubeosis of the iris
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Glaucoma
- An eye disorder requiring another eye procedure beforehand
- A missing iris
Furthermore, it’s important to note that undergoing this procedure for purely cosmetic reasons is not recommended and may even be prohibited. Leading organizations such as the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the Food and Drug Administration, most European Drug Administrations, and the American Glaucoma Society do not endorse it for non-medical purposes.
Are Colored Contact Lenses Risky?
Colored contact lenses used without a prescription pose certain risks, including:
- Corneal abrasions leading to severe inflammation
- Infections like keratitis
- Corneal ulcers
- Conjunctivitis
- Rare cases of blindness
Laser Eye Surgery for Eye Color Change: Is It Safe?
While the potential risks of laser eye surgery for changing eye color exist, they have not been definitively proven. Potential risks include:
- Uveitis due to potential inflammation caused by the laser beam
- Glaucoma
- Reduced vision
- Rare cases of potential blindness
Comments from various ophthalmologists’ societies in Europe and the United States suggest that potential patients should exercise caution and make informed choices about eye color-changing techniques before undergoing any procedure.
On the other hand, some positive feedback mainly comes from the Stoma Company, asserting the safety of the procedure after more than a decade of testing. However, these results are provided in the report submitted to the FDA.
While it is likely less risky than surgical procedures because it does not involve surgery, it still requires compliance and careful consideration.
Is Keratopigmentation Safe?
Keratopigmentation is a distinct procedure compared to the surgeries mentioned above, as it focuses on pigmentation rather than lenses, iris depigmentation, or iris alteration.
As with any surgical procedure, keratopigmentation may carry some risks, but the safety largely depends on factors such as the clinic, surgeon, protocol, and technology used. Therefore, keratopigmentation can indeed be safe if the following criteria are met:
- Confirm the equipment and laser provided by the clinic.
- Assess the background and experience of the surgeon.
- Ensure the safety of the pigments used.
In summary, keratopigmentation is considered one of the most effective methods for changing eye color. Opting for the right procedure, with the right ophthalmologist, team, laser, and pigment, can result in a safe and efficient eye color-changing technique.
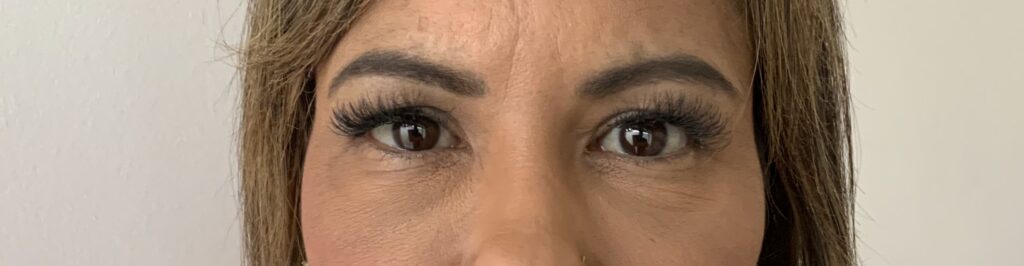
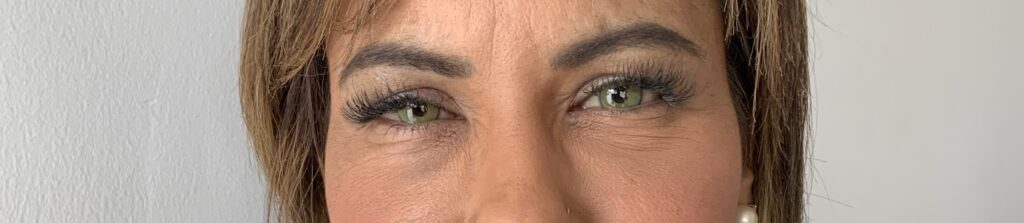
Sharing your medical history with your ophthalmologist is a valuable step in ensuring your safety during eye color-changing procedures.
Is Keratopigmentation a Safe Choice for Changing Eye Color?
When it comes to eye color-changing procedures, Keratopigmentation stands out as the safest option. In contrast, surgeries like eye depigmentation and artificial iris transplants are associated with significant risks.
However, it’s important to note that no surgical procedure is entirely without risks. To ensure your safety with Keratopigmentation, there are several factors to consider.
The Evolution of Keratopigmentation: A Journey of Discovery and Advancement
Understanding the history and evolution of Keratopigmentation sheds light on its safety and effectiveness. This technique, also known as corneal tattooing, has a rich history:
- The practice of corneal tattooing can be traced back to Galen of Pergamum in the 170s AD.
- In 1870, oculoplastic surgeons like Louis Von Wecker introduced the term “corneal tattooing” into medical literature.
- The modern era of Keratopigmentation was ushered in by American ophthalmologist Samuel Lewis Ziegler in 1922 through his work on “Multicolor tattooing of cornea.”
- In the 1990s, the development of corneal tunnels for intracorneal rings to manage conditions like keratoconus paved the way for introducing pigments.
- Spanish ophthalmologist Professor Alio played a pivotal role in 2001 by utilizing femtosecond lasers to create secure and precise tunnels, elevating the technique.
- Therapeutic keratopigmentation initially offered hope to patients with conditions such as aniridia, coloboma, traumatic iris injuries, or albinism, where iris staining was absent, and no adverse events were reported. This led to its expansion into the realm of aesthetics.
As is often the case with medical innovations, initial skepticism is common. Similar scenarios unfolded with other medical procedures, like rigid poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) implants in cataract surgery in 1949, phacoemulsification in cataract surgery in 1967, refractive surgery in the 1990s (with concerns about corneal scarification), and corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL) in 1997. However, these procedures are now widely accepted and have positively impacted millions of lives.
Keratopigmentation is no exception to this pattern of initial scrutiny. In 2021, during the annual congress of SAFIR (Society of the French Association of Implants and Refractive Surgery), Professor Muraine presented findings indicating that among various techniques, femtosecond laser-assisted Keratopigmentation posed the lowest risk. In contrast, laser depigmentation of the iris was associated with glaucoma and cataract risks, while iris implant placement led to corneal decompensation and necessitated corneal transplants.
In conclusion, the history and evolution of Keratopigmentation highlight its safety and effectiveness, with current evidence supporting it as the least risky option among various eye color-changing techniques.
Ensuring the Safety of Your Keratopigmentation: The 4 Crucial Criteria
- Certification of Your Ophthalmologist:
- It may seem obvious, but the first and foremost criterion is the expertise of the ophthalmologist performing your Keratopigmentation. Your ophthalmologist must hold board certification and demonstrate specialized training in Keratopigmentation. They should be transparent about their journey to becoming an expert in this field, including the number of surgeries they’ve performed and the specific techniques employed, along with the equipment used.
- Membership in a Scientific Association:
- Medical surgery, including Keratopigmentation, benefits from the knowledge-sharing among specialists. Just as a plastic surgeon belongs to a Board of Certified Plastic Surgeons like the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, your ophthalmologist should be part of a reputable scientific association. Being part of such an association signifies a commitment to sharing knowledge and experiences among peers, which is especially crucial for emerging procedures like Keratopigmentation. It ensures that the latest advancements are embraced. Therefore, among our criteria, we emphasize Eye Clinics and ophthalmologists who are affiliated with these international societies.
- Laser and Equipment Quality:
- Your ophthalmologist and their team must provide clear information about the type of femtosecond laser used to create the channel for pigment insertion in Keratopigmentation. While any ophthalmologist can claim to use the best or latest technology, it’s essential to verify this claim. Your ophthalmologist should utilize state-of-the-art lasers like the Zeiss brand. Older lasers, such as the VisuMax 500 in use in New York or the IntraLase brand, are inadequate. The latest technology, like the Zeiss VisuMax 800 employed by some of our certified Clinics for Keratopigmentation in Italy and France, is crucial. The reason is clear: outdated lasers can pose risks like subconjunctival hemorrhages and vision loss during the laser procedure.
- Quality and Stability of Pigments:
- Emphasizing the importance of pigment quality cannot be overstated in Keratopigmentation. It’s vital to avoid introducing non-certified components or even common food pigments into your eyes on a permanent basis. The comfort and quality of your vision hinge on this crucial factor. We’ve observed instances of surgeons worldwide using uncertified pigments, including some derived from everyday food items.
In summary, safeguarding the safety and success of your Keratopigmentation procedure involves rigorous adherence to these four criteria. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your chosen ophthalmologist, surgical team, equipment, and pigments meet the highest standards for a secure and effective eye color-changing experience.

